Uroflowmetry is a diagnostic procedure conducted to measure the flow of urine. It determines the speed at which the urine flows, the volume of urine that flows out, and how long it takes. All these metrics help to assess the functioning of your urinary tract and diagnose certain urinary disorders.
In this blog, we will help you understand the uroflowmetry test, how it is performed, and how to analyze the uroflowmetry test results to manage your urinary disorders.
What is a Uroflowmetry Test?
Also known as a urinary flow rate test, uroflowmetry is a non-invasive process to measure the flow of urine during urination. It records the speed and volume of urine expelled in milliliters per second (mL/sec).
Doctors prescribe this test to learn about your urine flow rate, probable urinary anomalies, functioning of the sphincters, bladder issues, and prostate problems.
The following measurements are checked in a uroflowmetry test:
- Maximum urine flow
- Time taken to reach maximum flow
- Average flow
- Total volume of urine expelled
- Flow time
- Discharge time
How is the Uroflowmetry Test Performed?
Unlike traditional urinary tests where the patients are asked to urinate into a small container, uroflowmetry involves urinating into a special toilet or a funnel-shaped device with a flask. This is called a uroflowmeter..
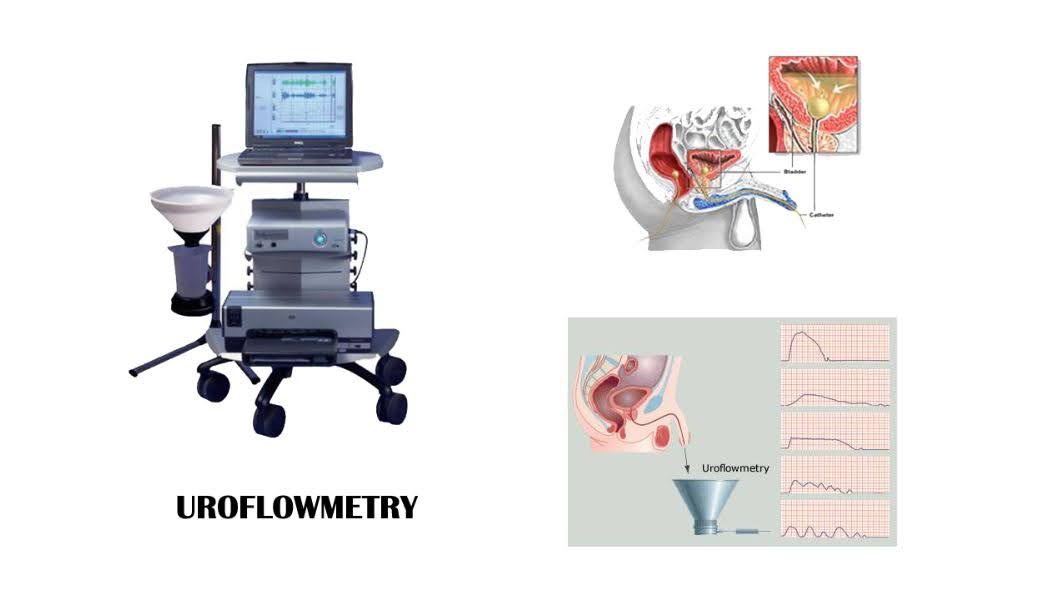
Image: Source
Patients are requested to urinate as normally as possible, i.e. without applying a lot of pressure or force as that may manipulate the flow or speed of the urine.
The uroflowmeter records the urine volume, the flow rate, the average and maximum flow, and the total time it takes until the bladder is empty. Most doctors use PC-based urodynamics equipment to record the results.
During normal urination, the initial urine stream commences slowly, speeds up, and then finally slows down again. The uroflowmeter device can easily record any differences from the normal urination values based on which your doctor will make a diagnosis.
Analyzing Uroflowmetry Test Results
The uroflowmetry test determines several parameters, including the maximum and average flow rate. This flow rate is calculated as milliliters (mL) of urine expelled per second.
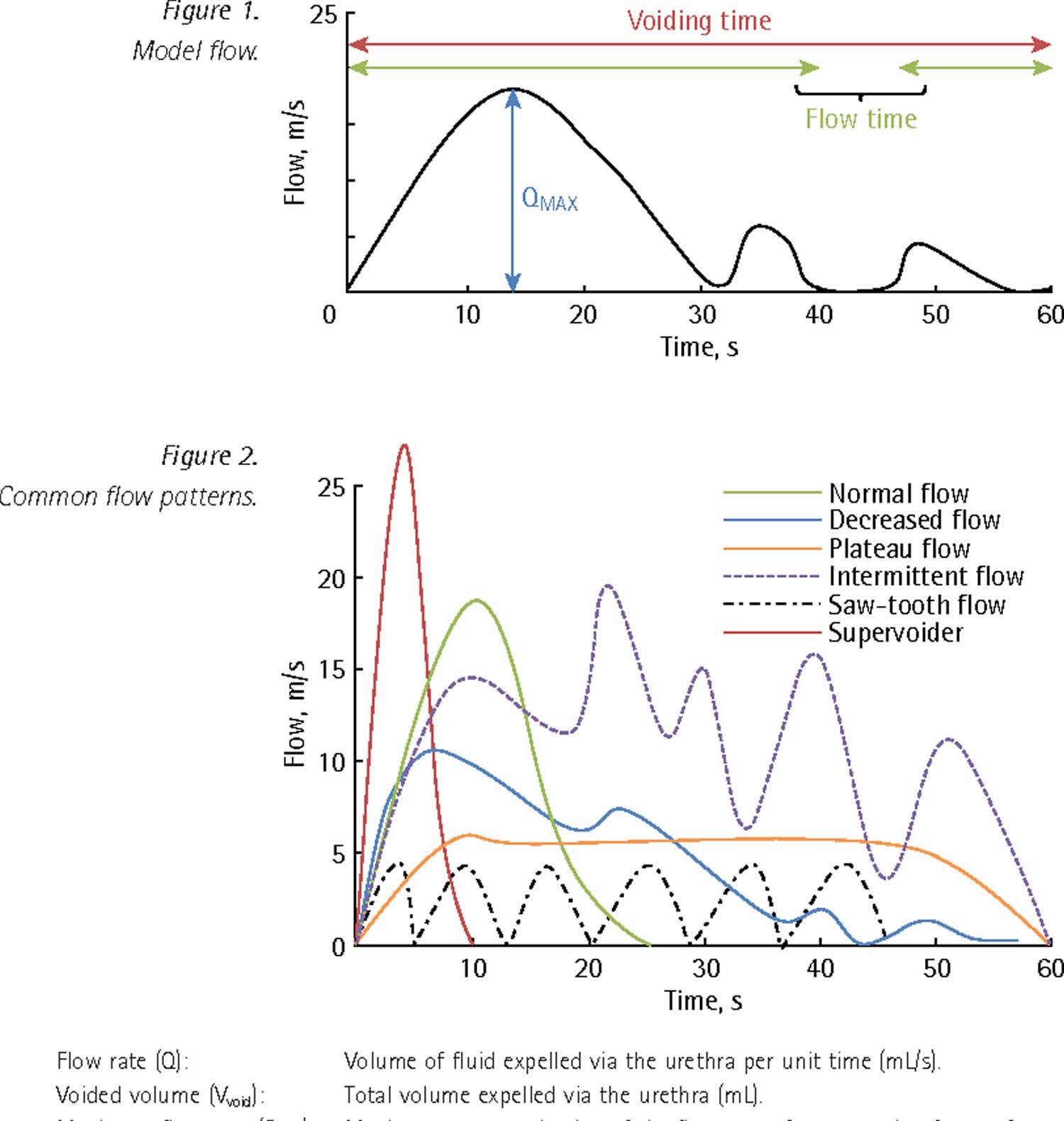
Image: Source
Let us first determine the normal values of uroflowmetry in men, women, and children. This will help you interpret your uroflowmetry test results more accurately.
Normal Values of Uroflowmetry in Men
In men, uroflowmetry values vary with age. For instance, in aging men, the flow of urine slows down due to prostate enlargement. Additionally, gradual weakening of bladder contractions or health issues such as diabetes can impact the uroflow, thus reducing the uroflowmetry values.
Moving on, normal uroflowmetry values in men are as follows:
- Aged 14- 45: Mean flow rate is 21 mL/sec
- Aged 46- 65: Mean flow rate is 12 mL/sec
- Aged 66- 80: Mean flow rate is 9 mL/sec
Normal Values of Uroflowmetry in Women
Unlike men, uroflowmetry values in women are not impacted by age. Thus, normal test values generally remain the same in women, which is:
- Aged 14- 45: Mean flow rate is 18 mL/sec
- Aged 46- 65: Mean flow rate is 18 mL/sec
- Aged 66- 80: Mean flow rate is 18 mL/sec
Normal Values of Uroflowmetry in Children
Sometimes, even children face bladder issues and are required to undergo a uroflowmetry test. The average uroflow test values for boys and girls are as follows:
- Children aged 4- 7: Mean flow rate is 10 mL/sec
- Boys aged 8- 13: Mean flow rate is 12 mL/sec
- Girls aged 8- 13: Mean flow rate is 15 mL/sec
Interpreting the Uroflowmetry Test Results
Your doctor will use the test results to determine your maximum flow rate, also termed Qmax. This flow rate along with your urine volumes and pattern of voiding bladder will determine the amount of blockage.
- If your Qmax is above 20 mL/sec, there is zero possibility of any obstruction.
- If your Qmax is between 15- 20 mL/sec, there might be chances of low obstruction. If the doctor suspects any blockage, he may advise further diagnostic tests.
- If your Qmax is between 10- 15 mL/sec, there is a high probability of an obstruction.
- If your Qmax is less than 10 mL/sec, there is a severe blockage. This may also indicate impaired bladder contractions.
Typically, conditions such as diabetes, prostate cancer, benign prostate enlargement, or bladder tumors can result in severe blockages.
Additionally, if the Qmax is extremely high, it may indicate weakened sphincters or issues like urinary incontinence. Many times, patients have to undergo surgery for prostate cancer or benign prostate enlargement. In most cases, after the surgery, the uroflow returns to normal values. However, in certain cases, there is permanent damage to the sphincters during the surgery that leads to urine leakage.
Lastly, the total volume of urine expelled is also a crucial parameter. Your doctor may recommend further investigation if the volume is less than 100 mL. This may include a post-void residual measurement using a bladder scanner.
Conclusion
Uroflowmetry is a non-invasive process that offers a detailed urine flow analysis. The procedure only takes a couple of minutes to complete and helps to identify various urinary tract conditions such as urinary incontinence.
The uroflowmetry test results along with other clinical assessments will guide healthcare professionals in providing a suitable care and treatment plan for individuals with urinary concerns. At Santron Meditronic, we offer best-in-class urodynamic equipment that ensures accurate diagnostic test results. Our ISO 13485-certified uroflowmeters are made with the highest-quality components, certifying patient-centered care.








